Published: Jan 14, 2020 by Dev-hwon
Data similarity(데이터 유사도)
데이터 유사도란 두 데이터가 얼마나 같은지 나타내주는 척도이다.
Basic data structure
- data matrix (n object X p attributes)
- similarity matrix (n objects X n objects)
- disimilarity matrix (n objects X n objects)
- sim(i,j) = 1 - d(i,j)
Similarity and Distance Measures
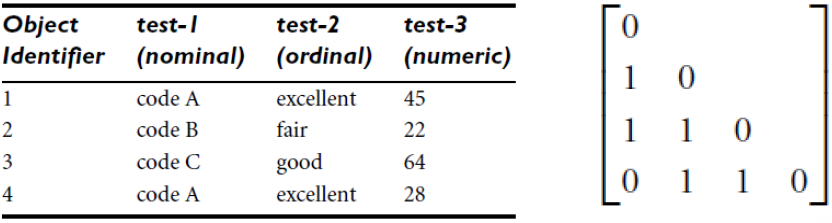
1. For nominal attributes
- \[d(i,j) = { {p-m} \over p }\]
- m = number of matches
- p = total number of attributes descibing the objects
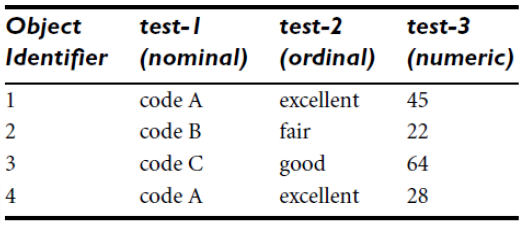
ex)
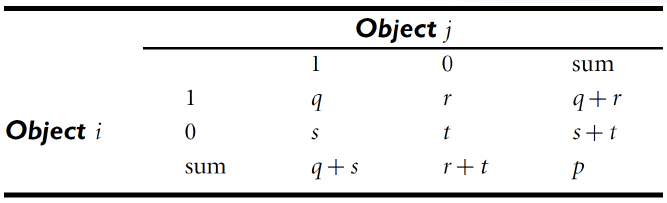
2. For binary attributes
- For symmetric binary attributes (0과 1 모두 중요)
- For asymmetric binary attributes (1이 더 중요)
\(d(i,j) = { {r+s} \over {q+r+s}}\) (Jaccard Coefficent라고도 불림)
(ex)
3. For numeric attributes
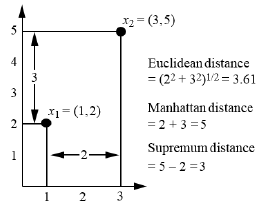
1) Euclidean Distance
\[d(i,j) = \sqrt{\sum^p_{k=1}(x_{ik}-x_{jk})^2}\]2) Manhattan Distance
\[d_{manhattan}(i,j) = \sum^p_{k=1}\left | x_{ik}-x_{jk} \right |\]- Euclidean, Manhattan Distance가 만족해야하는 조건
- 음이 아닌 수
- Identify of indiscernibles
- 대칭
- Triangle inequality
3) Minkowski Distance
\[d(i,j) = (\sum^p_{k=1} \left | x_{ik}-x_{jk} \right |^r)^{1/r}\]- r=1 : Manhattan (L1 norm)
- r=2 : Euclidean (L2 norm)
- r= \(\infty\) : Supremum (Lmax norm, L\(\infty\) norm)
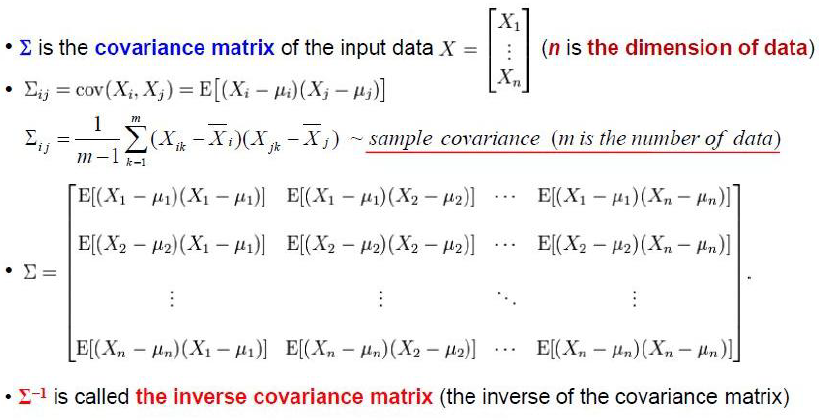
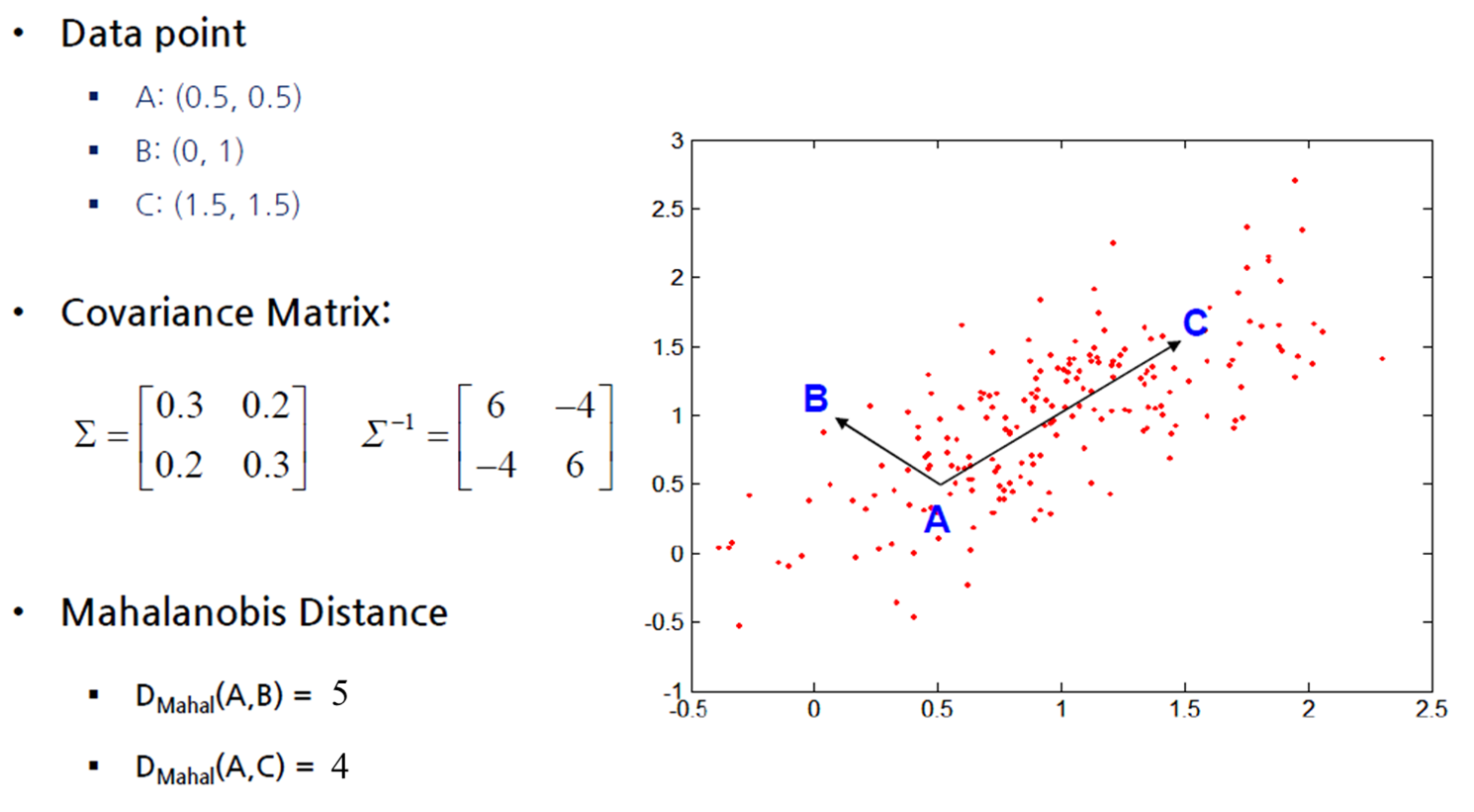
4) Mahalanobis Distance
- 데이터 분포를 고려하기 위해 사용
4. For ordinal attributes
- ordinal attributes는 순서 or 순위가 있지만 크기는 알 수 없다.
- 1) 등급에 따라 점수를 준다.
- 2) normalizes
- 3) Euclidean Distance 이용
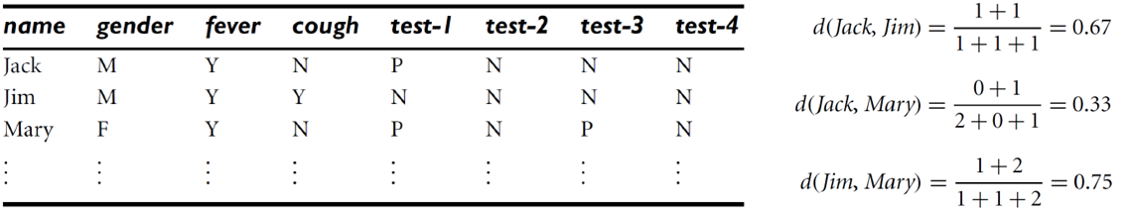
5. For mixed attributes
1) 각 속성 유형을 그룹화하고 각 유형에 대해 개별적으로 군집화와 같은 데이터 마이닝 수행하는 방법
2) 모든 속성 유형을 함께 처리하여 한 개의 분석을 실행하는 방법 -> 여러 속성을 단 한개의 차이 행렬로 연결하고 모든 의미 있는 속성을 공통된 범위 척도 [0.0, 1.0]으로 만드는 방법
\[d(i,j) = { {\sum^p_{f=1}\delta_{ij}^{(f)}d_{ij}^{(f)} \over \sum^p_{f=1}\delta_{ij}^{(f)}} }\]\(\delta_{ij}^{(f)}=0\)일 때,
1) \(x_{if}\)나\(x_{jf}\)가 없는 경우 2) \(x_{if}=x_{jf}=0\)이고 속성 f가 비대칭 이진값 \(d_{ij}^{(f)}\)인 경우
- if f is numeric:
\(d_{ij}^{(f)} = { {\left | x_{if} - x_{jf} \right |} \over max_h x_{hf} - min_h x_{hf} }\)
- if f is nominal, binary or ordinal: 따로 구하는 방법과 같음
cosine similarity(코사인 유사도)
- 내적공간의 두 벡터의 유사도를 측정함
- 두 벡터간 각도의 코사인으로 측정하며 두 벡터가 동일한 방향을 향하고 있는지 여부를 판단
- 종종 텍스트 분석에서 문서의 유사도를 측정하는데 사용
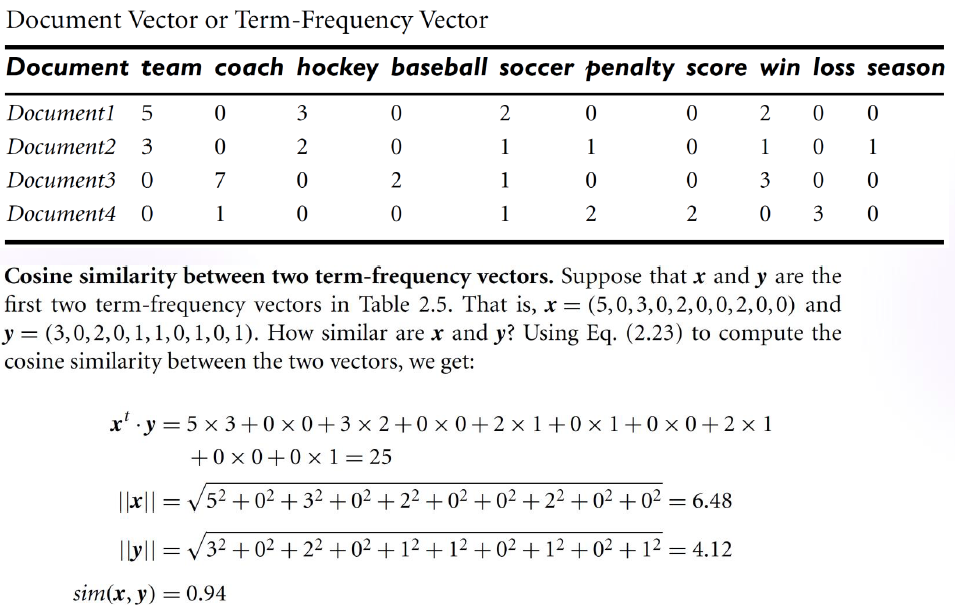
Term-Frequency 벡터
- 일반적으로 매우 길고 데이터 값은 별로 없음, 따라서 대부분 0의 값을 가짐
- 일반적으로 거리 측정값은 희소한 숫자형 데이터에 대해서는 적합하지 않음
- 따라서 2개의 문서가 공통으로 보유하고 있는 단어와 해당 단어의 발생 빈도에 초점
\(sim(x,y) = {x\cdot y \over \left \| x \right \| \left \| y \right \|}\), \(\left \| x \right \|\)는 벡터 x에 대한 유클리드 노름, difined as \(\sqrt{x_1^2+x_2^2+\cdots}\)
ex)
속성이 이진값일 때
- 코사인 유사도는 공유된 특성이나 속성으로 해석
- \[sim(x,y) = { {x\cdot y} \over {x\cdot x + y\cdot y - x\cdot y} }\]
- x 또는 y가 소유한 속성의 수에 대해 x와 y가 고유한 속성의 개수 비율
- 타니모토계수나 타니모토 거리라고 함